Ohm's Law Calculator for Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Power
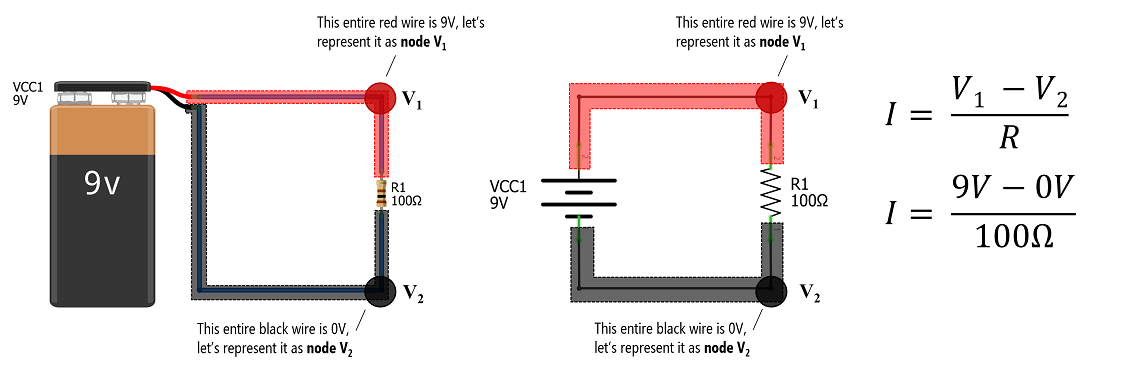 Ohm's Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and physics, describing the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. It states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance between them.
Ohm's Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and physics, describing the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. It states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance between them.
Ohm's Law Equation : V = IR, where V is the voltage across the conductor, I is the current flowing through the conductor and R is the resistance provided by the conductor to the flow of current.
- If you increase the voltage (Volt) in a circuit while the resistance is the same, you get more current (Amp).
- If you increase the resistance (Ohm) in a circuit while the voltage stays the same, you get less current.
If two of these values are known, technicians can reconfigure Ohm's Law to calculate the third. Just modify the pyramid as follows:
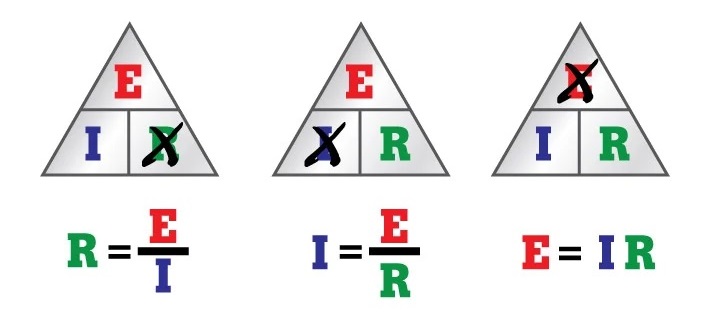
If you know voltage (E) and current (I) and want to know resistance (R), X-out the R in the pyramid and calculate the remaining equation (see the first, or far left, pyramid above).
Note: Resistance cannot be measured in an operating circuit, so Ohm's Law is especially useful when it needs to be calculated. Rather than shutting off the circuit to measure resistance, a technician can determine R using the above variation of Ohm's Law.
Now, if you know voltage (E) and resistance (R) and want to know current (I), X-out the I and calculate the remaining two symbols (see the middle pyramid above).
And if you know current (I) and resistance (R) and want to know voltage (E), multiply the bottom halves of the pyramid (see the third, or far right, pyramid above).
Try a few sample calculations based on a simple series circuit, which includes just one source of voltage (battery) and resistance (light). Two values are known in each example. Use Ohm's Law to calculate the third.